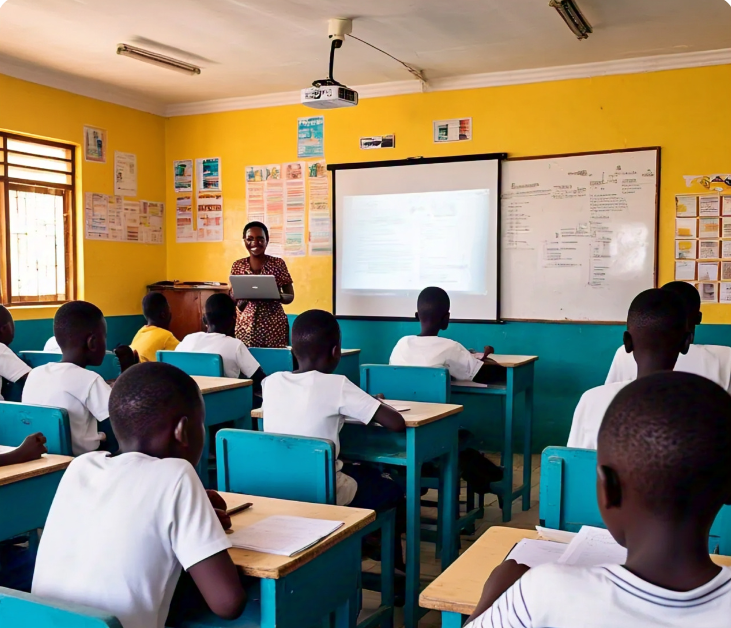
Schools in Uganda encounter numerous challenges that affect the quality of education provided. These issues span infrastructure, teaching practices, resource availability, and teacher preparedness, significantly impacting learning outcomes and student engagement.
One major issue is the lack of science laboratories or their inadequate equipping. Science education relies heavily on experiments and practical demonstrations, but without proper facilities, students are confined to theoretical learning, which limits their understanding and application of scientific principles. Similarly, the shortage and high cost of instructional materials like textbooks, laboratory apparatus, and teaching aids make it difficult for schools to provide comprehensive learning experiences. This scarcity forces teachers to rely on outdated resources, further hindering the quality of education.
Teaching methods in many schools are predominantly teacher-centered, where students passively absorb information without active participation. Lessons are often theoretical, focusing on recall rather than understanding or applying knowledge, which stifles critical thinking and creativity. Many concepts taught, particularly in science and mathematics, are abstract and difficult for students to grasp without visual aids or practical demonstrations, leaving them disconnected from the subject matter.
The shortage of qualified teachers is another critical challenge, with rural areas being the most affected. This shortage is compounded by a gender imbalance, especially in science subjects, where there are few female teachers to serve as role models for young girls. Additionally, teacher absenteeism and low motivation remain persistent issues, often caused by poor remuneration, lack of professional development, and challenging working conditions. These factors reduce the effectiveness of teaching and disrupt the learning process.
A significant challenge is the generation gap between teachers and students. Many teachers rely on traditional teaching methods, while students, often referred to as “dot.com learners,” expect modern, technology-integrated approaches. This disconnect affects communication and student engagement, as the teaching methods do not align with the learners’ expectations and experiences. Overcrowded classrooms further exacerbate the situation, making it difficult for teachers to provide individualized attention or supervise practical activities effectively.
Students also struggle to see the relevance of what they learn in class to real-world applications. This perceived disconnect leads to a lack of interest and engagement, especially in subjects like physics, chemistry, and mathematics. Teachers, in many cases, are driven by the pressure to complete the syllabus rather than ensuring students thoroughly understand the material. This “finishing the syllabus syndrome” results in superficial learning, where students are prepared for exams but not equipped with practical knowledge or critical thinking skills.
Another challenge is the lack of professional development opportunities for teachers. Many educators are not exposed to modern teaching practices or technology integration, leaving them unprepared to adapt to new educational demands. Visual aids and models, which are essential for making lessons engaging and effective, are also rarely used due to limited resources or lack of training.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach. Investments in infrastructure, such as building and equipping science laboratories and libraries, are crucial to supporting practical learning. Schools need access to affordable instructional materials to ensure that students and teachers have the resources they need. Teachers should adopt learner-centered approaches that encourage active participation and hands-on learning, making lessons more engaging and impactful.
Providing professional development opportunities for teachers can equip them with modern pedagogical skills and strategies for integrating technology into their teaching. Recruiting and supporting more female teachers in science and other underrepresented areas can help address gender imbalances and inspire young girls. Improving teacher motivation through better pay, benefits, and working conditions is also essential to reducing absenteeism and enhancing their commitment to teaching.
Reducing class sizes by employing more teachers will enable more effective supervision and personalized attention for students. Connecting classroom concepts to daily life experiences can make learning more relevant and engaging for students, fostering a deeper understanding of the material. These efforts, combined with the active involvement of stakeholders, have the potential to transform Uganda’s education system into one that promotes critical thinking, innovation, and real-world readiness in learners.
bullstresser zstresser.su
stresser Table of ContentsStresse.ruAmplification Methods in Stresser ServicesProtecting Against DDoSGrabify Tools and Their Impact Innovations in Stresser Technology We offer powerful Layer 4 and Layer
stormer.su hard stresser
stresser Table of Contents Stresser.su, the Ultimate Choice for Free IP Stresser, Booter, and Leading Layer 7 Services. The Role of IP Stressers IP Grabbers
Take the first step towards finding your perfect gay sugar daddy on craigslist today
Take the first step towards finding your perfect gay sugar daddy on craigslist today Craigslist is a great resource for finding your perfect gay slot
Connect with compatible black singles
Connect with compatible black singles Are you in search of a black senior dating internet site that suits singles within generation? if that’s the case,
POMEM GİRİŞ ŞARTLARI Bitlis Polis Meslek Eğitim Merkezi
POMEM GİRİŞ ŞARTLARI Bitlis Polis Meslek Eğitim Merkezi Buraya, sistemde güncellediğiniz e-posta adresini girerek, e-posta adresinize yeni bir aktivasyon linki gönderilmesini sağlayabilirsiniz. BTprod yeni girişAktivasyon
Türkiye’de Bir casinomhub Casino Seçme Nedenleri
Türkiye’de Bir casinomhub Casino Seçme Nedenleri Türkiye’de çevrimiçi bahis ve casino sitelerine yönelik istek her geçen gün artmaktadır. Bu ihtiyaç, üstün oranlar, geniş oyun yelpazesi