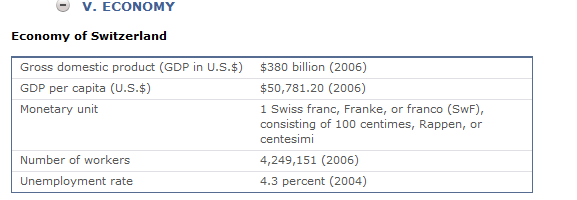
Economic Activities in Switzerland
The Swiss in recent years have brought their economic practices largely into conformity with the European Union to enhance their international competitiveness.
Although the Swiss are not pursuing European Union membership in the near term, in 1999. Bern and Brussels signed agreements to further liberalize trade ties. These agreements still have to pass a Swiss referendum in spring 2000, however. Switzerland is still considered a safe haven for investors, because it has maintained a degree of bank secrecy and has kept up the franc's long-term external value.
AGRICULTURE
Only 10% of the total area of Switzerland is ideal for Arable farming. The mountains cover a very large area composed of bare steep slopes and the soils on the upper slopes are thin and not suitable for crop cultivation, however, on these upper slopes the availability of pasture has facilitated the development of livestock farming.
The climate also restricts farming activities in Switzerland, The growing season is short limiting the crops that can be grown and snow-cover limits farm activities for three months each year.
In addition, avalanches are a serious problem that often damages the crops. Inspite of the unfavourable climatic conditions, Switzerland produces almost 60% of her food requirements.
The country is self sufficient in milk, cheese, potatoes and pork. Switzerland also produces large amounts of wheat, poultry products as well as beef.

Swiss Alps
Vineyard
Mountainous terrain, poor soils, and a cold climate inhibit agricultural development in Switzerland. Farming is generally confined to small family operations, such as this vineyard in the Alps. Here terracing enables the farmers to contend with the steep mountain slopes.
Factors favouring Agricultural Activities in Switzerland,
Climate: The country enjoys different climatic conditions in different regions. This has made it possible for farmers to grow different types of crops as well as carry out livestock farming.
The cool temperate climate for example has facilitated animal husbandry especially dairy farming as well as the growing of potatoes. The Mediterranean climate has promoted fruit growing in some areas of Switzerland like Ticino region.
Fertile soils in some areas of Switzerland: the river valleys have alluvial soils which are ideal to crop growing and moraine deposits are also responsible for the fertile soils in the plateau region.

Making Chocolate
A worker ensures quality control at a chocolate factory in Switzerland. Switzerland is famous for its fine chocolate, especially milk chocolate-a by-product of the nation's dairy farming industry.
There is enough pasture to promote livestock farming on the upper slopes of the mountains. In winter, when the outdoor feeding is Impossible, the animals are fed on fodder and hay.
Availability of market: Much of the food produced is consumed Internally but some surplus is sold because Switzerland is in a region which is densely populated thus there is, available market for the different products.
An efficient transport network: There is most especially the good railway network connecting farmlands to trading and marketing centres. This factor has greatly influenced livestock farming.
Availability of capital: This is utilized by the farmers to buy all the necessary equipment so as to improve on their farming activities. This is a very strong factor especially where market gardening and fruit growing are concerned.
Livestock Rearing
The climate of Switzerland favours the growing of pasture but in addition fodder crops are grown for example sugar beet.

The Jura and the Alps provide natural pasture during the summer months and these are important regions for livestock rearing. In these regions, transhumance is practiced and is altitudinal. Transhumance is the practice of movement with animals from one area to the other following changes in season. They move upslopes during summer and down slopes during winter.
The livestock management in Switzerland is of high quality. This is because of the highly skilled veterinary personnel and government support in form of subsidies.

Livestock rearing in the Jura
Since the soils of the Swiss Jura are rather poor and infertile, they are thus not suitable for arable farming. Arable farming refers to crop growing. So livestock farming prevails. Sheep, goats and cattle are reared. However, the cow is the most important animal kept in this region.
Sheep and goats are kept on the higher ridges and terraces which have rather poor pastures. The cattle are left to graze of the ridges and valley floors.
The cool moist summers provide ideal conditions for dairy farming and the main products from the region are butter and cheese.
Livestock Rearing in the Alps
In the Alps, dairy farming is the most important activity. Zero grazing is practiced as well as transhumance. Milk is transported in churns, tank lorries and polythene pipelines to co-operative dairies.
Livestock rearing on the Swiss plateau
On the plateau, in addition to cattle, sheep and goats, pigs are also reared, however, cattle out number the other forms of livestock and pigs come next in importance.
Due to lack of adequate pasture especially during winter, goats and sheep are of less importance. The dairy products from the plateau are butter, milk and cheese. Wool and mutton from sheep and pork from pigs are also important.
Arable Farming
Crop cultivation in Switzerland takes up a very small percentage of the land use. The major forms of arable farming include;- cereal cultivation, market gardening, fruit growing and viticulture,
Cereal cultivation
Involving the cultivation of barley, wheat, oats and maize. Cereal cultivation occupies two thirds of the cropland. The flat plateau with its fairly fertile soils as well as the sunny rainy summers favour the growth of cereals.
Market gardening
This takes up 20% of the total cropland and the farmers supply two thirds of the country's vegetable requirements.
The major crops grown include potatoes, cabbages, onions, beans, and peas. These crops are grown near urban centres and the market is provided by the hotel industry as well as the urban population in the large urban centres.
Fruit growing
This is another important farming activity. The major fruits grown include plums, apples, cherries, apricots and straw berries. There are large orchards found the province Valais in the Eastern part of the country and the areas surrounding the numerous lakes in the country. The fruits are either canned or used in jam making.
Viticulture is possible.
This is the growing of grapes used in the making of wine. It is important in the Rhone valley, in the Northern shores of Lake Geneva and also the shores of lake Neuchatel. The south Ticino are also important for viticulture.
Importance of agriculture
Problems Facing Agriculture
These problems include the following:
Only 10% of the total area is good for crop cultivation. This is due to the mountainous nature of the country. A large part of the country has steep slopes.
The soils on the steep slopes are thin and infertile and therefore not good for cultivation of crops.
The climate restricts farming activities. The growing season is short and this is mainly in summer. This limits the crops which can be grown.
The transportation of agricultural products is difficult especially in the mountainous regions.
The occurrence of avalanches is a serious problems as they damage crops.
Read
the passage below and answer the questions that follow:
"Switzerland
is a landlocked country with just over 6,000,000 inhabitants. Only a quarter of
the land is cultivable and there are few mineral resources of importance.” Adapted
from: Hughes, D Randle Handle; The Rhine Basin, A study of development.
(a) (i)
What is meant by the term, "land locked country"?
(ii)
Explain how Switzerland has tried to solve the problem of being a landlocked
country.
(b)
Giving specific examples describe how physical factors have made it difficult
to cultivate the remaining % of Switzerland.
(c)
State three ways in which the uncultivable land in Switzerland has been put to
use.
(d)
(i) Name any two minerals mined in
Switzerland.
(ii)
Explain how Switzerland has been able to develop her industries
inspite of having few mineral resources of importance.