Introduction to the Rhinelands
.png)
General Objective:
By the end of the topic, the learner
should be able to describe the location, position and size of the Rhinelands.
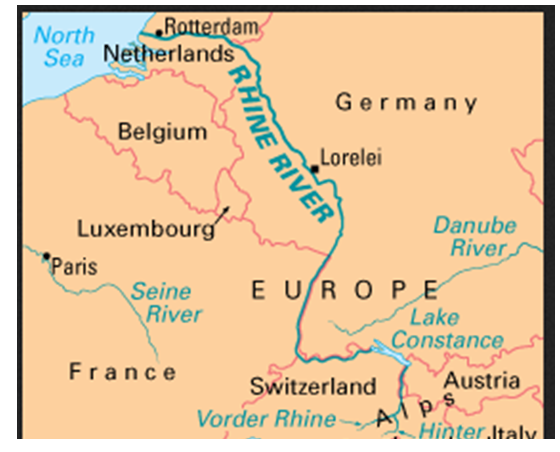
In this section of the Rhine Basin, we shall be examining the countries that are drained by the River Rhine. The Rhine river has its source in Switzerland at St. Gotthard Pass, flows through Germany, making a border with France. It continues northwards and forms boundaries between Belgium and Netherlands and finally pours its water into the North Sea.
The Rhine
(German: Rhein; Dutch: Rijn; French: Rhin; Italian: Reno; Romansh: Rain; Latin: Rhenus; Spanish: Rin) is one of the longest and most
important rivers in Europe at 1,320 kilometres (820 mi), with an
average discharge of more than 2,000 cubic meters per second.
The five Rhineland countries include; Switzerland, Germany, Netherlands, Luxembourg and Belgium. These countries are connected through the Economic union of Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg. In short the Benelux countries.
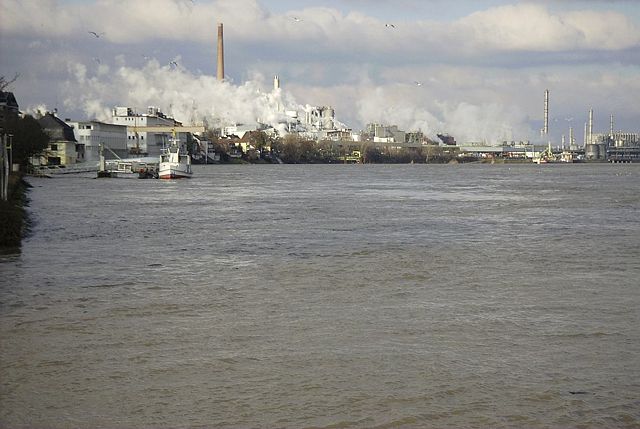

Rhine with chemical industry at Wesseling near Cologne. (Source:
www/wikip/images/789/78934.jpg.htm
The Rhinelands is a European region, which borders North Sea in north, Czechoslovakia in the East, Italy In the south and France in the west. In terms of size, the Rhinelands cover an area of about 360, 000 sq. Km. This area is smaller than Kenya and slightly bigger than Uganda.
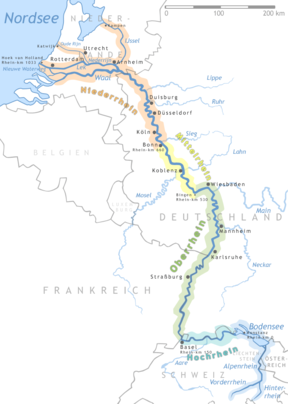
River Rhine Passes
through all the Five Rhineland Countries.

The Rhine canyon (Ruinaulta) in Graubünden in Switzerland.