Introduction to Germany
Germany is officially known as the Federal Republic of Germany (Deutschland in German language) It is a country in Central Europe bordered to the north by the North Sea, Denmark, and the Baltic Sea; to the east by Poland and the Czech Republic; to the south by Austria and Switzerland; and to the west by France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands. The territory of Germany covers 357,021 km² and is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. With over 82 million inhabitants, it comprises the largest population among the member states of the European Union and is home to the third-highest number of international migrants worldwide
The republic of Germany is now one country having been united in 1989.
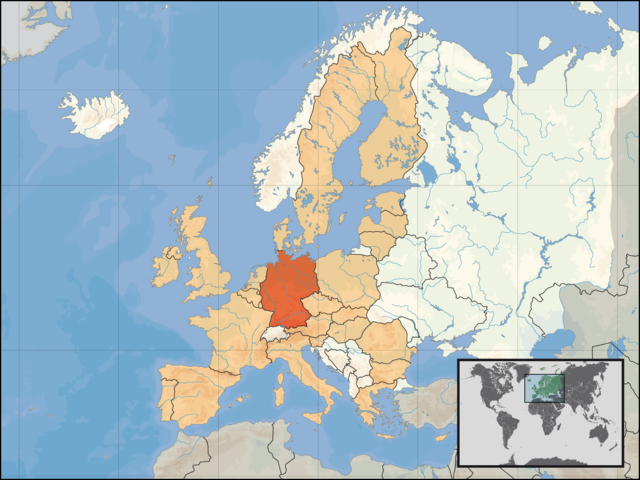
It is now a combination of West Germany and East Germany which were separate countries after the World War II.
Germany is a major industrialized country and one of the richest countries in the world. In fact it is the fourth most richest country after US, UK and Japan.
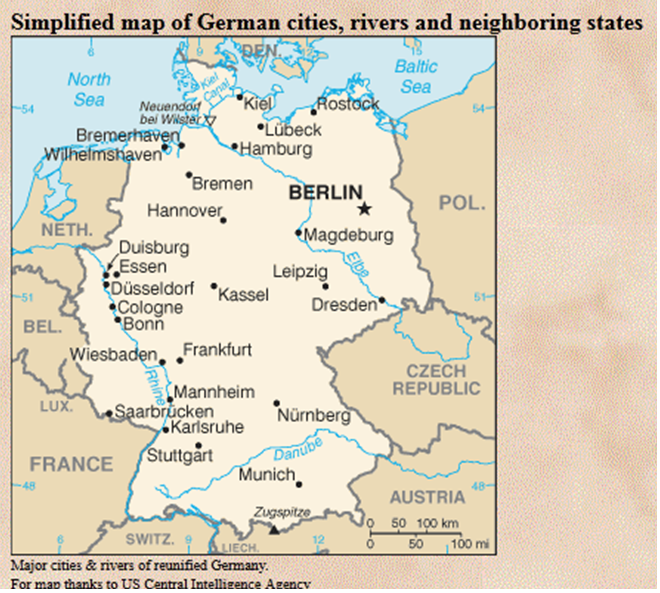
Located in the center of Europe it borders the Netherlands. Belgium, Luxembourg, and France on the west; Switzerland and Austria in the south; the Czech Republic and Poland in the east, Denmark in the north; and the Baltic Sea on the northeast.
The official capital and largest city is Berlin, but many administrative functions are still carried on in Bonn, the former capital of West Germany.

Germany has developed because the Germans had to start almost afresh after World War II. The whole economy including her major cities were destroyed when Adolf Hitler involved the whole world in a major war between 1939 and 1945.