The Economy of Luxembourg
Luxembourg has a surprising variety of economic activity and possesses a degree of prosperity which is unusual in view of its restricted size. Although farming employs the most people, mining and metallurgical industry are the and the country is virtually dependant on the production of steel.
Steel production is her chief industry and which absorbs most of the country's workers. It accounts for about 75% of the National income. Her industries include locomotive, Motor vehicles, machinery and machine tools. Roll stock, farm implements, chemicals, rubber, plastics.
Her raw materials pass via the Albert canal through Antwerp from Belgium and Rotterdam seaport via the Rhine River.
Agriculture is carried on by about half the population and it is the principal occupation. The chief crops are wheat, oats, potatoes and beetroot, Viticulture is practiced and some excellent sparkling wines are produced. There are over 15,000 acres of meadow and pasture land and considerable numbers of pigs and cattle are reared.
Manufacturing industry, however, is not highly developed although there are some manufactures of textiles, gloves, leather, tyres and pottery.
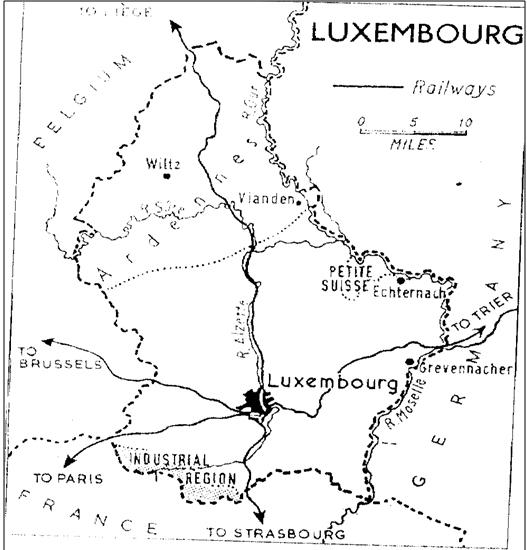
Luxembourg occupies a strategic position and the city of Luxembourg has become an international railway centre.
Luxembourg's stable, high-income economy features moderate growth, low inflation, and low unemployment. The industrial sector, which was dominated until the 1960s by steel, has become increasingly more diversified to include chemicals, rubber, and other products.
During the past decades, growth in the financial sector has more than compensated for the decline in steel. Services, especially banking and other financial exports, account for the majority of economic output. Agriculture is based on small, family-owned farms.
Luxembourg has especially close trade and financial ties to Belgium and the Netherlands (see Benelux), and as a member of the EU it enjoys the advantages of the open European market. Luxembourg possesses the highest GDP per capita in the world (US$87,995 as of 2006), the twelfth highest Human Development Index, and the fourth highest quality of life.[ As of March 2006, unemployment is 4.8% of the labour force. For the fiscal year of 2005 and 2006, Luxembourg has run a budget deficit for the first time in many years, mostly because of slower international economic growth.
Luxembourg City
It is the capital city of Luxembourg and has a population about 120,000 people. It is a metropolis" of the country as well as an Administrative city.
It is a gathering place for diplomats from many nations, with embassies. Ministries, parks and Public buildings. Though the city's streets and Buildings have a German look but all signs are French. French is the popular language.
Map of Luxembourg
Luxembourg's Close Economic Links with Belgium
The steel industry has long been one of the main branches of Belgium in the Belgo - Luxembourg Economic Union (BLEU) the steel industry of crucial importance. As producers the two countries only account for a modest share of the total output. In 1968, they produced 11.6 and 4,8 tons respectively, out of the Worlds total of 530 million tons.
Among the world's significant exports of steel products, the BLEU come second to Japan. The Economic cooperation and integration existing between the two countries is beyond mention and has achieved a lot of commercial benefits for Luxembourg as a country.