The Concept of continental drift
![]()
The term continental drift refers to the movement of continental blocks relative to one another across the surface of the earth to their present positions to create continents and ocean basins. The theory of continental drift was based on rifting and drifting of individual landmasses. The theory says the sialic masses emanated from the split of Pangea and they started moving in various directions.
Rupturing and drifting started abut 250
million years ago – first split into Laurasia
and Gondwanaland with the former further breaking into Northern continents and
the latter forming southern continents.
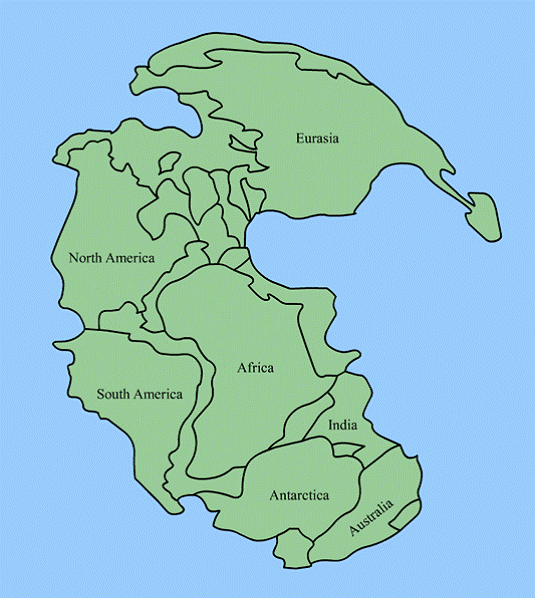
Figure 1: The continents fit together
like pieces of a puzzle. This is how they looked about 200 million years ago.
A study of the globe would
perhaps real among other things that if the Americans were pushed Eastwards
they would almost fit into the shape formed by the coasts of Africa and
(a)Hypothesis before the
idea of continental drift became accepted as possible.
The moon theory, the moon theory and the convection currents
theory.
(b) Hypothesis after
continental drift theory was widely accepted as possible.
·
F.B Taylor’s theory of continental drift
·
Alfred Wegner’s theory of
Continental drift.
·
H. Hess’ sea floor spreading theory
·
Plate tectonics theory.
There movements that have
been advanced to explain the distribution of continents. However, only four will be considered for academic purposes.
Perhaps the first man to
propose the continental drift theory was Francis Bacon in 1620 when he noted
the Jigsaw – like fit between the East coast of south America and the West
African coast. In 1668 RP. Francis Placet
went further to suggest that prior to the floods
In 1885 Antonio Snider went
even further than Bacon and Placet by drawing two maps of the world. One showing a reconstruction of the world
before drifting and the other showing the present day distribution of the
continents.
At the end of the nineteth
century, the Austrian researcher Edward Suez produced the theory that had once
been part of a super continent which he named Gondwanaland after the Gondwana
region in