Other theories for Continental Drift.
There are a number of
theories which were put forward before the theory of continental drift came
into existence. These theories include
the :
·
Convectional currents theory
·
Tetrahedral hypothesis(or the
contracting earth hypothesis)
·
The moon theory
·
The expanding earth theory
·
Isostacy
·
Polar wandering theory
Isostatic re –
adjustment theory:
There is a belief that
continents and ocean basins were formed as a result of isostatic readjustments
of the continental rock that Pangaea was composed of rock of varying densities
where some rocks were very dense and heavy while some areas had lighter rocks.
The differences resulted into the upwarping of areas with lighter rocks
and formed the continents (sialic). The
dense and heavier rocks led to down warping some areas that formed ocean
basins.
Rock expansion
theory:
It is believed that the Pangaea split as a result of
excessive environmental temperatures which was followed by the cracking of the
Pangaea into several continental landmasses and their eventual drifting apart.
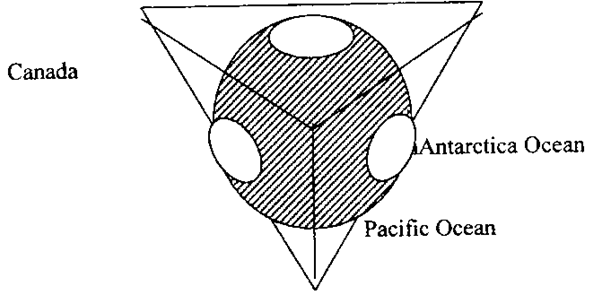
Tetrahedral hypothesis:
This theory does not involve
horizontal crystal land mass movement but
vertical movements. It releases
on the belief that the earth is contracting .
It is stated that any given surface expresses greatest volume in a
sphere and small volume on a tetrahedron.
That the earth would shrink on Geli a way that the ocean basin would be
depressed on the tetrahedral faces while the continental crusts would occupy
the remaining faces. The arrangement of
continents into 3 pairs and ocean basins make the earth resemble a tetrahedron.
Gravitational pull of the earth so thought to be the
basis for the earth contraction whereby materials are pulled to the earth’s
interior which cause the earth to become smaller. The theory was criticised.
The expanding
earth theory:
This emphasises horizontal movement of the crustal
landmasses. That the earth was originally
smaller and as the interior of the earth expanded, thus forced outer crustal
materials to break forming continental plates and as the earth continued to expand, the bigger the
gaps became and further plates drifted from earth other.
Polar
Wandering:
In the 1950s, physicists in England
Scientists measured the
orientation and direction of the acquired magnetic fields and, from these
orientations, calculated the direction of the rock’s magnetism and the distance
from the place the rock was found to the magnetic poles. As calculations from
rocks of varying ages began to accumulate, scientists calculated the position
of the earth’s magnetic poles over time.
The position of the poles varied depending on
where the rocks were collected, and the idea of a polar wander path began to
form. When sample paths of polar wander from two continents, such as North
America and
In summary, Polar wandering theory
explains latitudinal changes through which the continents have passed. It suggests that the earth crust with the
mantle migrate as a whole relative to the earth’s axis but remains fixed
relative to the star eg if Africa moves
a metre in a certain direction, even other continents follow the same distance
on the same direction. It was highly
criticized too.
The moon
theory:
The theory tried to explain why there is missing
sialic crust on the floor of the ocean basins, that the moon separated
itself from the earth early in the
history of the solar system. The theory
formed on the earth’s surface before the moon was born, then much of the crust
must have been carried away by the moon
when the great rapturre took place.
It was Osmand Fisher (1881)
who first suggested that the huge Pacope basin must be a scar
left behind when the moon separated itself from the earth. It was supported for two reasons.
Materials of the moon
reflect sunlight in the same way that powdered sialic materials do. They are therefore similar materials with
possibly the same origins.
The Pacific basin is the
largest region from which sialic materials are lacking. If 1/3 of the earth’s surface and the size of
the moon is about 1/3 of the earth. It
is possible that the pacific basin is the huge hole (scar) left behind when the
moon separated from the earth.
Evidence Of Continental Drift.
To
justify his continental drift theory, Alfred Wegner Marshalled an impressive
amount of evidence, facts and opinions, most of which have proved too true to
be denied. Other researchers have added
on the amount of evidence.
Geometrical fitting (jig – saw /visual fit).
The present of continental
margins is such that most of the continents have geometric shapes that would
fit into each of forced close. Thus jig
– saw fit of continents were at one time together forming Pangea but they
merely split to other parts eg fitting the Eastern coast of South America in the

Geological similarities.
Similarity on rocks is another evidence used to
justify continental drift. There are
remarkable similarities between rocks found in different landmasses of the
southern continents. In Africa the rocks
of Ghana and Cameroon
share common characteristics with those of Brazil
on South America . It therefore suggests that those areas were
once of the same continent. This evidences constituents what is commonly
known as “matching geology”.
Presence of fold mountains.
This seems to suggest that
continents have been moving towards each other because when the tectonic plates
collide with other, land masses on them
may fold and lead to the formation of
fold mountains. Atlas and Alps ranges,
Himalayas in
Paleotological Evidence(Historical Fossils).
The existence of historical
fossils and other rock types where climatic conditions do not favour
theory formation also suggests that
continental drift took place. The
following are the examples: In the
In the same way, rocks of
Furthermore, the existence
of Petroleum, coal and other organic minerals in the extreme Northern
Hemisphere as an indication of continental drift. This is because coal, petroleum are meant for
tropical areas.
Vegetation.
The similarity of the vegetation
and animals in different continents, which seem to have been attached to each
other suggests the occurrence of
continental drift, eg the Brazilian tropical rainforests and the
Occurrence of Laterite.
The occurrence of Laterite
on North America and certain parts of
Dwyka Tillites:
Studies from Palaeclimatology have provided further
evidence that justifies continental drift.
This is in convection with glacial deposits. Dwyka Tillites are the glacial carboniferous
rocks are found on many parts of the former Gondwanaland which proves that
these continents were once together.
Palaegmanetism evidence.
Palemagnetism refers to the
ancient or fossils magnetism on
rocks. It is established from the geological laboratory that research
or rocks of the earth crust which are always magnetized by the earth’s magnetic
field at the time of formation. They show real North and South.
Magnetic Field Reversals
In 1963, British scientists
Fred J. Vine and Drummond H. Matthews combined their observations of the marine
magnetic anomalies with the concept of reversals of the earth’s magnetic field.
They proposed that the marine magnetic anomalies were a “tape recording” of the
spreading of the ocean floor as the earth’s magnetic field reversed its
direction. At the same time, other geophysicists were studying lava flows from
many parts of the world to see how these flows revealed the record of reversals
of the direction of the earth’s magnetic field. These studies showed that
nearly four reversals have occurred over the past 5 million years. The concept
of magnetic field reversals was a breakthrough that explained the magnetic
polarity switches seen in seafloor spreading as well as the concept of similar
magnetic patterns in the rocks used to demonstrate continental drift.
However when Pangea split
up, the rock changed position and the direction of the magnetic north of the
individual pieces of rock changed.
Sea floor spreading evidence:
Research has sown that most sea floors are expanding
and many oceans and seas are becoming bigger.
This is probably because of the movement of continents eg the Red sea enlarged to 300 km wide in the 200 million
years. The ocean ridges on the middle
oceans are reported to be expanding eg the Great Atlantic ridge is said to be
expanding and the Atlantic
ocean ’s enlarging
Expansion of the E. African Rift valley and the
The E. African rift valley
is expanding proving that continents are in the state of motion as a result of
compressional and tensional forces within the earth’s crust. About 1000 million years the rift valley was
not there. It widens at a rate of about
2 – 3 cm/ year.

Similarity of oil beds.
It has been found out that
the oil beds of
Criticisms of evidence of continental drift.
Some researchers have given
different views discrediting the contribution of Wegner and people who
contributed to the theories of continental drift. They argue that:
1. The spreading of ocean
floors might be because of continuous erosion of the mainland, which makes the
oceans appear as if they are expanding.
2. The similarity in the rocks
might because of the same climatic conditions eg Equatorial climatic for the
case of
3. The presence of coral rock
on different continents and the existence of identical vegetation on different
continents might be because f the increasing world temperatures.
4. The presence of glacial
tillites material on the
5. The above criticisms show
that there are some weaknesses on theories of Wegner. However some are real and therefore the
theory should not be under estimated.