Topic 1: Characteristics of Living Organisms
What is Biology?

The word 'Biology' comes from two Greek words: Bios, which means 'life' and Logos, which means 'to study'. So Biology is the study of living things. Living things are also called organisms. Examples of living things include:
- bacteria,
- amoeba,
- worms,
- mushrooms,
- snails,
- insects,
- birds,
- fish,
- snakes,
- cows,
- people and trees.
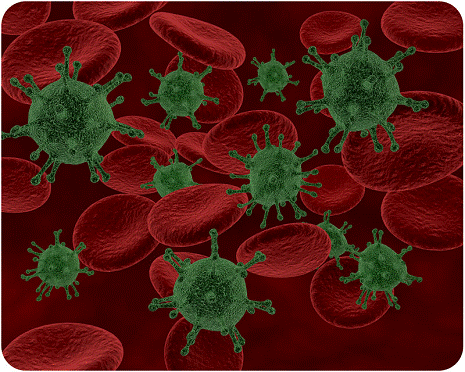
Is this picture a colorful work of abstract art, or is it something else? Imagine shrinking down to a tiny size, so small you could enter a blood vessel. The picture shows what you might see rushing toward you. Do you know what the red objects are? If you guessed red blood cells, you are right. What about the knobby green objects? Watch out for these! They are viruses that have invaded the blood. When you read this book, you will take an exciting journey into the realm of blood cells, viruses, and just about everything else that is related to life. You will learn how your own body works, what makes living things unique, and what you and viruses have in common. This first chapter explains how scientists learn about the natural world and introduces you to biology, the science of life.
There are living things all round you; in the waters, in the air, on the earth and under the earth. Some are so tiny you cannot see them without a microscope. Others, like the elephant, the whale, and the trees of the forests, are considerably bigger than you are. Living things not only show great variation in size, they also vary much in appearance and their ways of life.
Biology examines the structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, and distribution of living things. It classifies and describes organisms, their functions, how species come into existence, and the interactions they have with each other and with the natural environment.
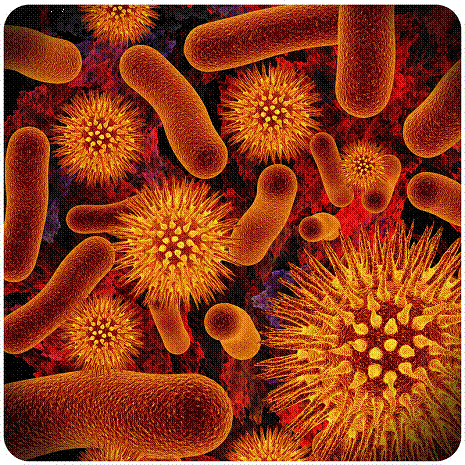
How do we tell the difference between a living thing and a non-living thing? Think about your own body. How do you know that you are alive? Your heart beats. You breathe in air. Do all living things need to do be like you in order to be "alive"?
The image on the side represents bacteria. Do these bacteria look like they could be alive? They do not have hands or feet or a heart or a brain, but they are actually more similar to you than you may think. Scientists found that all living things share certain characteristics. In this chapter, we will discover how to precisely define living things.
Man has long been interested in the living things around him.
Firstly, because he cannot exist without them. They supply his food, and often the materials he uses for clothing and shelter.
Secondly, plants and animals appear so interesting, with so much to be found out about them, that some people cannot resist studying them to satisfy their curiosity.
Importance of Biology
As you work through your biology course, you will come to realise why the scientific study of life is of such importance to us all.
Firstly, man himself is a living being, and the more we know about life, and living things in general, the better we can understand our own bodies and how they work in health and disease.
This is why a study of biology is considered essential in the education of a medical doctor.
Secondly, if we are to continue to produce more food for ourselves, it is necessary to find out all we can about plants and animals: for example, how they grow and develop, how they breed, and how they sometimes become diseased. A training in biology is obviously essential for the various agricultural sciences. ,
Thirdly, during the present century,""-the population of the world has been increasing at an unprecedented rate. This is largely because we have begun to apply our knowledge of biology to medicine and agriculture. One result is that nowadays fewer people die in epidemics.
People who do study biology are called biologists (Gk: bios, life). Scientists who specialise in the study of plants alone are called botanists, while those who study only animals are called zoologists.
Branches of Biology
There are two major branches of Biology, namely Botany and Zoology.
Botany is a branch of Biology, which deals with the study of plants for example ferns, trees.
Zoology is a branch of Biology, which deals with the study of animals for example hydra, worms, insects, fish, birds and lions.
Four unifying principles form the foundation of modern biology: cell theory, evolution, genetics and homeostasis.
Biology as a separate science was developed in the nineteenth century, as scientists discovered that organisms shared fundamental characteristics. Biology is now a standard subject of instruction at schools and universities around the world.
Most biological sciences are specialized disciplines. Traditionally, they are grouped by the type of organism being studied: botany, the study of plants; zoology, the study of animals; and microbiology, the study of microorganisms. The fields within biology are further divided based on the scale at which organisms are studied and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the fundamental chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions of systems of biological molecules; cellular biology examines the basic building block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of the tissues and organ systems of an organism; and ecology examines how various organisms and their environment interrelate.
We can study Biology by looking at the structure of organisms also called anatomy; or by considering how their structures function or Physiology.