CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS
From early time, man has found it convenient to group together, or classify, animals and plants. Many of his groupings are based on utility, or the sharing of a common feature. For example, all types of trees which provide him with orange, sweet-tasting fruits might be associated in his mind.
Living things are classified by dividing them into different kingdoms for example the animal kingdom, the plant kingdom, etc.
Each kingdom is further divided into different phyla for example the animal kingdom is divided into the vertebrates phylum, the arthropods phylum, etc.
Each phylum is further divided into different classes for example the arthropod class is divided into the crustecean class, the arachnid class, the myriapod class and the insect class.
Each class is further divided into different orders for example the insect class is divided into the two-winged Diptera order, the social-casted Hymnenoptera order, the hard-winged Orthoptera order.
Each order is further divided into different families and each family is divided into different genera.
Each genus is then divided into different species.
Members of a species can carry out free reproduction to produce fertile offspring.
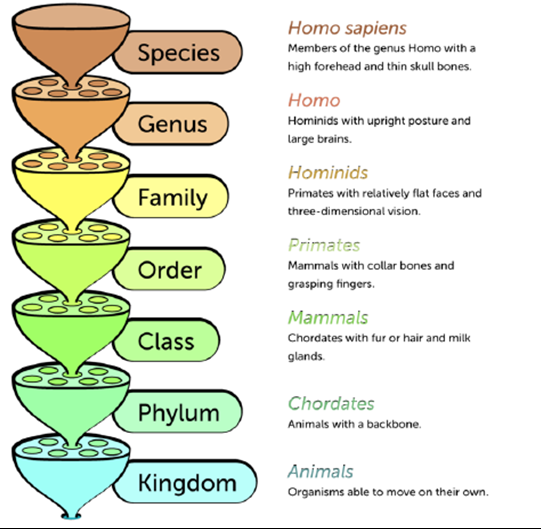
FIGURE 2.18
This diagram illustrates the classification categories for organisms with the broadest category Kingdom at the bottom and the most specific category.
Classification of man:
|
NAME |
GROUP |
EXAMPLES |
|
KINGDOM |
ANIMALIA |
Insects, fish, cow, apes, monkey, early man, modern man |
|
PHYLUM |
VERTEBRATE |
fish, cow, ape, monkey, early man, modern man |
|
CLASS |
MAMMALIA |
cow, monkey, ape, early man, modern man |
|
ORDER |
PRIMATE |
monkey, ape, early man, modern man |
|
FAMILY |
HOMINIDAE |
ape, early man, modern man |
|
GENUS |
HOMO |
early man, modern man |
|
SPECIES |
SAPIENS |
modern man only |
|
|
|
|
Classification of maize:
NAME GROUP EXAMPLES
KINGDOM PLANTAE Mosses, liverworts,
ferns, pine, beans,
sorghum, corn, maize
PHYLUM TRACHEOPHYTA ferns, pine, beans,
sorghum, corn, maize
CLASS SPERMATOPHYTA pine, beans, sorghum,
corn, maize
ORDER ANGIOSPERM beans, sorghum, corn, maize
FAMILY MONOCOTYLEDON sorghum, corn, maize
GENUS ZEA corn, maize
SPECIES MAYS maize
Naming of organisms (nomenclature):
Organisms are given common names and scientific names.
Examples of common names are cat, dog, maize. Such common names are misleading because: They are based on superficial resemblances; and secondly, they can refer to many different organisms in different localities.
The standard system of naming organisms used in Biology is called the binomial system.
This method of naming animal and plant types by giving each a double Latin name was developed by Linnaeus, a biologist of the eighteenth century. It is now used by biologists throughout the world. The first of the two is called the generic name, and the second the specific name. It is conventional to write the generic name with a capital letter and the specific name with a small letter.

FIGURE 2.19 These children are all members of the same species Homo sapiens.
The genus name is written starting with a Capital letter and the species name is started with a small letter; and both names are printed in italics.
The
'cat' genus is called Felis; the
following are the scientific names of the different cats:



Felis domestica domestic cat Felis tigris tiger Felis leo lion
Felis pardus leopard
The identification (dichotomous) key
This is the key used to identify organisms quickly and accurately. The key commonly used is the Numbered Couplet Key. In this key, each number refers to a characteristic with two contrasting traits of an organism or organisms. An organism with a unique trait is identified and if there are two or more organisms with that trait, they are referred to the next steps where they will be identified individually.
To
illustrate the identification key, we shall use the following fowls:![]()
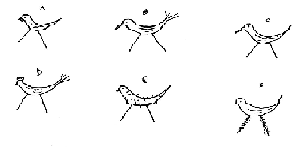
A: Has a wattle, Has a short beak
B: Has a long beak, Has tail feathers
C: Has a long beak
D: Has a comb, Has tail feathers,
E: Has fluffy feathers
F: Has a wattle, Has feathery legs
So the dichotomous key (numbered couplet) would be:
1. Has fluffy feathers .......................... E
Has smooth feathers ....................... 2
2. Has a comb ................................... D
Has no comb... ............................ 3
3. Has feathery legs ............................ F
Has featherless legs ........................ 4
4. Has tail feathers ................................ B
Has no tail feathers ........................... 5
5. Has a long beak ................................ C
Has a short beak ............................... A
For
the following drawings of insects, an identification key can be made:
A: Has long antennae B: Has a long style, has long antennae
C: Has hairy antennae, Has short antennae
D: Has short style, Has long antennae
E: Has no style,- Has no antennae
F: Has a long style,- Has long antennae- Has hairy antennae
An identification key (numbered Couplet) could be constructed as below:
1. Has antennae .................. E
Has no antennae .............. 2
2. Has long antennae ............ 3
Has short antennae ........... C
3. Has hairy antennae ........... F
Has smooth antennae......... 4
4. Has style ....................... 5
Has no style ................... A
5. Has long style .................. B
Has short style ................ D
1. Which of the following is not a kingdom in the classification of living things?
A: Monera B: Fungi C: Protista D: Plantae
2. Select the organism that belongs to a different class from the others.
A: Flea B: Mite C: Scorpion D: Tick
3. Which of the following cannot be used to put plant specimens into different groups? .
A: Shape of leaves. B: Size of leaves
C: Type of venation D: Type of root system
4. A scientific name consists of two words. To which groups do they belong?
A: Genus and class B: Genus and order
C: Genus and species D: Genus and family
5. The following organisms are made up of cells except
A: Amoeba B; Tapeworm C: Virus D: Yeast
6. The following characteristics are found in Arthropods. Which one is only found in some?
A: Exoskeleton B: Segmented bodies
C: Compound eyes D: Jointed limbs
7. Which of the following features is not characteristic of rnonocotyledonous plants?
A: Parallel venation B: Leaf sheath
C: Soft stem D: Tap root
8. The following organisms have scales except
A: Catfish B: Dove C; Tilapia D: Tortoise
9. Select the animal that has different types of teeth (is heterodont).
A: Gecko B: Monkey C: Toad D: Vulture
11. A student viewed a specimen on a slide using a microscope. He used a x 10-eye piece and a x40 objective. The magnification of the image he saw was
A: x4 B:x50 . C:x400 D:x410
12. A number of organisms of different species living in a particular locality is called
A: A community B: A population
C: An ecosystem D: A habitat