Introduction
The term coast is used to denote the zone of contact between the land and the sea. African coastline is about 27000 km only. It is shorter compared to Europe’s.

The coastal lands constitute only a small part of African continent. Much of Africa’s coastal line is very smooth; that is to say there is absence of deep indentations typical of European coastline. No well defined peninsular, no large Estuaries and off shore islands are very few. In certain sections, the smoothness of the coast is broken down by rias.
Map of Africa showing Coastline types
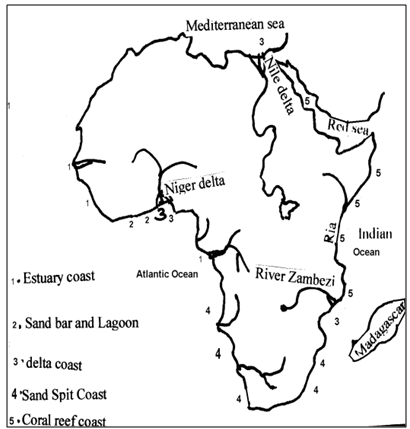
A ria is formed when sea level rises and water from the sea or ocean invades and occupies low parts of the landscape especially along river valleys. Rias can be sited at Freetown in Sierra Leone and Mombasa.
It is important to note that coastal features are a result of different processes that take place at the sea.
The three main coastal processes are:
- Wave or marine erosion and deposition.
- Sea level changes that is, rise and fall also known as emergence and submergence.
- The last one is coral formation.