KAWA MULTIMEDIA PUBLICATIONS
Fault scarp (Escarpment)
This is a steep slope where the land falls from a higher to a lower level. It is caused by vertical earth movements along a fault line that develops in the crust of the earth. Examples of fault scarps in Africa are the following:
- Bamenda scarp in Cameroon,
- Ethiopian scarp, one of the greatest and the steepest,
- Butiaba scarp in Uganda,
- Manyara scarp in Kenya,
- Mau scarp in Kenya,
- Chunya escarpment, North of Mbeya between Lake Tanganyika and L. Malawi as well as
- the Elgaya escarpment
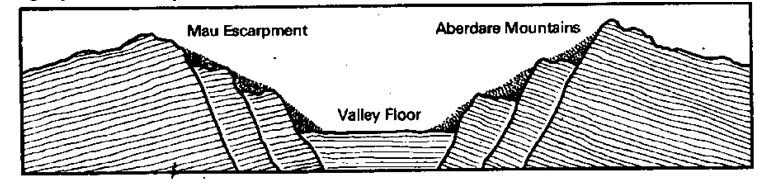
These steps can be seen near Nairobi in Kenya. The steps are partly hidden by soil. The dots show this.
Fault line scarp:
This is an escarpment or steep slope which has been greatly eroded and there is now no evidence of faulting i.e. the original fault scarp has been removed through erosion. They are common in South Africa and Madagascar.
Fault guided valleys:
This is a long straight river valley formed by a shattered zone along the lines of weaknesses or fault lines. Faults cause the rocks to be shattered and crushed which means that such rocks are easily eroded than those further from the fault.
As a result, rivers will tend to follow the areas of weaknesses and curve out straight valleys known as fault guided valleys. Main examples in Africa include the following:
- Santa river in Guinea,
- River Nile in Sudan,
- River Aswa in Uganda,
- Imo river in south East Nigeria and
- Weinsterg river in South Africa.
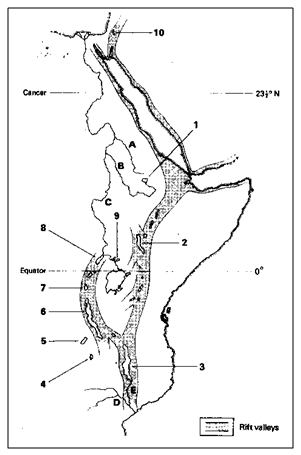
From the map below, name the lakes 1-10. Name rivers A to E (refer to the Atlas)