Elements of a good map
In
Primary four you learnt about maps. Do you remember how you defined a map? A
map is a drawing of a particular place showing land forms, plant cover and
other important features.
A
map can also be defined as a representation of a place or an object drawn as
seen from above.
A
picture is a representation of an object drawn as seen from
the sides.
Activity
Draw maps for the following object
|
Table
|
………………………… |
House |
………………… |
|
Tree
|
……………………… |
Basin |
………………… |
|
Bottle
|
……………………… |
Ball |
………………… |
|
Car |
……………………… |
Box |
………………… |
A
good map must have elements that help someone to read it easily. These elements
can also be called features and these include the following:- title or heading,
map key, scale, compass rose or direction, frame or boundary.
Title
A
title is a name or heading to the map. A title gives general purpose of the map
or it tells what the map is all about. For example, the title can be; a map
showing Physical features, Vegetation or climate east, South Sudan in the
north, Rwanda in the south west,
Tanzania in the south and the Democratic
Republic of Congo in the West.
What difficulty would a map reader find
if a map has no title?
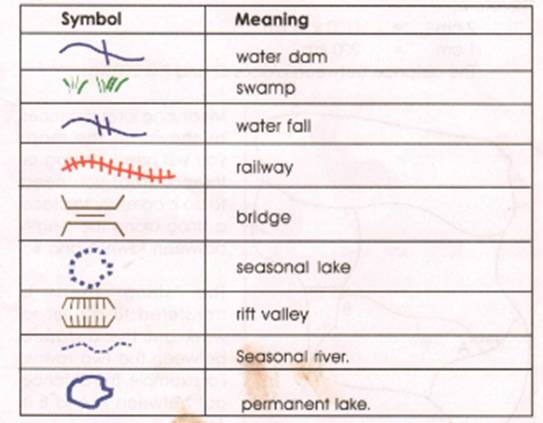
Key
A
map key which is sometimes called a map legend shows what symbols on a map stand
for. Symbols are signs that are used to represent the actual large features or
objects on a map.
A
key gives the interpretation of the symbols and signs used on
Examples of symbols and their
meaning
Map scale
A
map scale is the relationship between the distance on the map and actual
distances on the earth's surface. It compares a distance on a map with a
distance on the ground.
A
map scale helps you to find the real distance between places on a map. Each map
in this book has a scale that shows Kilometres.
You
can measure the distance on a map using a string and a ruler. For example, The
distance in centimeters measured between two places P and Q for instance it can
be 2cm.
Therefore,
you can find the distance in kilometres using the scale
given
below. 1 cm represents 100km.
1
cm = 100km
Therefore,
2 cm =
(100 x 2) km
1 cm =
200 km
The distance between places Q and P is 200 km
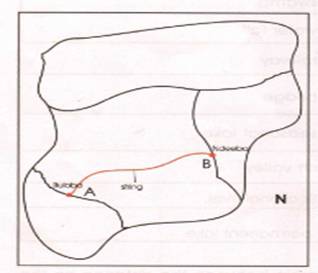
Measuring long distances as shown on the map, you will need a string or

Then
4 cm between town A and B will be 4cm = (4 x 4) km
= 16km.
The
distance from town A to B is 16 km.
A
frame or boundary is a border or the outside edge, of a place.
Which two countries share an international border with?
Uganda?
Compass rose or
direction
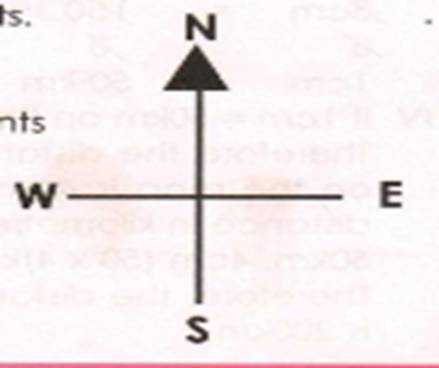
A
compass rose or direction is used to show the direction of an area from a given
point. Do you remember what you learnt about a compass rose in P.4?A compass
rose has four main points called Cardinal or primary Points and four Semi Cardinal points.
The
cardinal points are 90° from each other while semi cardinal points
are
45° from each cardinal point.
Activity:
1.
Draw map symbols for the following features on a map
(a) Quarry
(b) Factory
(b) Power generation station.
On a
sheet of paper, draw a compass rose and label the cardinal and semi cardinal
and semi cardinal directions.
3. Use the map
scale given ![]()
Step
1 Place the string against Apac and Kayunga
and mark the start and end
Of it.
Step
II Place the string against the ruler to
measure its length . The
measurement taken show the
length between Apac and Kayunga
Step
III Check the scale given, if it is linear scale
the first work out to find what
1cm represents
For example :
3cm represent 150 km
3cm =150
3 3
1cm =
50km
Step
IV If 1cm=
50km on the scale.
Therefore the distance between Apac and Kayunga on the map is 4cm.
Since you have to find out the
distance in kilometres, then the distance
Will be 1cm = 50km, 4cm (50x
4)km = 200km
Therefore, the distance between Apac and
Kayunga is 200km.
Key words
Location : Is where something is found.
Cardinal: Are directions north, east, west and
south.
Globe: Is a model of the earth.
Neighbor: Something or someone that is close
to a particular place or person.
Direction: The way something is moving or
facing.
Longitude: Imaginary lines that run from north
to south on a map or globe
Latitude: Imaginary lines that run from East
to west on a map.
Exercise 1
1. Construct
simple sentences using the following words;
a)
Direction b) neighbour
c)
Compass d) Latitude
2. What
is a map?
3. Why
is a title important on a map?
4. Why
are symbols important on a map?
5. Draw
a map symbol for a rift valley.
6. Name
the compass point marked Y
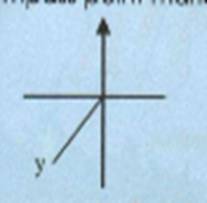
7. Which
African country lays West of Uganda?
8. Why
is the Equator marked 0°?
9. Mention
the method used to locate places on a map.
10. What is a landlocked country?
11. State one problem Uganda faces as a landlocked
12. Suggest one way in which Uganda has overcome the Problem of
being
landlocked.