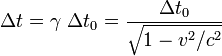Time dilation
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Time dilation is the phenomenon whereby an observer finds that another's clock which is physically identical to their own is ticking at a slower rate as measured by their own clock. This is often taken to mean that time has "slowed down" for the other clock, but that is only true in the context of the observer's frame of reference. Locally (i.e., from the perspective of any observer within the same frame of reference, without reference to another frame of reference), time always passes at the same rate. The time dilation phenomenon applies to any process that manifests change over time.
In Albert Einstein's theories of relativity time dilation is manifested in two circumstances:
- In special relativity, clocks that are moving with respect to an inertial system of observation (the putatively stationary observer) are found to be running slower. This effect is described precisely by the Lorentz transformation.
- In general relativity, clocks at lower potentials in a gravitational field — such as in proximity to a planet — are found to be running slower. This gravitational time dilation is only briefly mentioned in this article but is described elsewhere (see also gravitational red shift).
In special relativity, the time dilation effect is reciprocal: as observed from the point of view of any two clocks which are in motion with respect to each other, it will be the other party's clocks that is time dilated. (This presumes that the relative motion of both parties is uniform; that is, they do not accelerate with respect to one another during the course of the observations.)
In contrast, gravitational time dilation (as treated in General Relativity) is not reciprocal: an observer at the top of a tower will observe that clocks at ground level tick slower, and observers on the ground will agree. Thus gravitational time dilation is agreed upon by all stationary observers, independent of their altitude.
Contents
|
[edit] Overview
The formula for determining time dilation in special relativity is:
where
 is the time interval between two colocal events (i.e. happening at the same place) for an observer in some inertial frame (e.g. ticks on his clock),
is the time interval between two colocal events (i.e. happening at the same place) for an observer in some inertial frame (e.g. ticks on his clock),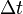 is the time interval between those same events, as measured by another observer, inertially moving with velocity v with respect to the former observer,
is the time interval between those same events, as measured by another observer, inertially moving with velocity v with respect to the former observer, is the relative velocity between the observer and the moving clock,
is the relative velocity between the observer and the moving clock, is the speed of light, and
is the speed of light, and is the Lorentz factor.
is the Lorentz factor.
Thus the duration of the clock cycle of a moving clock is found to be increased: it is measured to be "running slow." The range of such variances in ordinary life, where v / c < < 1 even considering space travel, are not great enough to produce easily detectable time dilation effects, and such vanishingly small effects can be safely ignored. It is only when an object approaches speeds on the order of 30,000 km/s (1/10 of the speed of light) that time dilation becomes important.
Time dilation by the Lorentz factor was predicted by Joseph Larmor (1897), at least for electrons orbiting a nucleus. Thus "... individual electrons describe corresponding parts of their orbits in times shorter for the [rest] system in the ratio :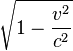 " (Larmor 1897). Time dilation of magnitude corresponding to this (Lorentz) factor has been experimentally confirmed, as described below.
" (Larmor 1897). Time dilation of magnitude corresponding to this (Lorentz) factor has been experimentally confirmed, as described below.
[edit] Experimental confirmation
Time dilation has been tested a number of times. The routine work carried on in particle accelerators since the 1950s, such as those at CERN, is a continuously running test of the time dilation of special relativity. The specific experiments include:
[edit] Velocity time dilation tests
- Ives and Stilwell (1938, 1941), “An experimental study of the rate of a moving clock”, in two parts. The stated purpose of these experiments was to verify the time dilation effect, predicted by Lamor-Lorentz ether theory, due to motion through the ether using Einstein's suggestion that Doppler effect in canal rays would provide a suitable experiment. These experiments measured the Doppler shift of the radiation emitted from cathode rays, when viewed from directly in front and from directly behind. The high and low frequencies detected were not the classical values predicted.
-
 and
and  =
= and
and 
- i.e. for sources with invariant frequencies
 The high and low frequencies of the radiation from the moving sources were measured as
The high and low frequencies of the radiation from the moving sources were measured as  and
and 
- as deduced by Einstein (1905) from the Lorentz transformation, when the source is running slow by the Lorentz factor.
- Rossi and Hall (1941) compared the population of cosmic-ray produced muons at the top of a mountain to that observed at sea level. Although the travel time for the muons from the top of the mountain to the base is several muon half-lives, the muon sample at the base was only moderately reduced. This is explained by the time dilation attributed to their high speed relative to the experimenters. That is to say, the muons are decaying about 10 times slower than they would in a rest frame (that is, for "stationary observers").
- Hasselkamp, Mondry, and Scharmann (1979) measured the Doppler shift from a source moving at right angles to the line of sight (the transverse Doppler shift). The most general relationship between frequencies of the radiation from the moving sources is given by:
-
- as deduced by Einstein (1905)[1]. For
 (
( ) this reduces to fdetected = frestγ. Thus there is no transverse Doppler shift, and the lower frequency of the moving source can be attributed to the time dilation effect alone.
) this reduces to fdetected = frestγ. Thus there is no transverse Doppler shift, and the lower frequency of the moving source can be attributed to the time dilation effect alone.
[edit] Gravitational time dilation tests
- Pound, Rebka in 1959 measured the very slight gravitational red shift in the frequency of light emitted at a lower height, where Earth's gravitational field is relatively more intense. The results were within 10% of the predictions of general relativity. Later Pound and Snider (in 1964) derived an even closer result of 1%. This effect is as predicted by gravitational time dilation.
[edit] Velocity and gravitational time dilation combined-effect tests
- Hafele and Keating, in 1971, flew cesium atomic clocks east and west around the Earth in commercial airliners, to compare the elapsed time against that of a clock that remained at the US Naval Observatory. Two opposite effects came in to play. The clocks were expected to age more quickly (show a larger elapsed time) than the reference clock, since they were in a higher (weaker) gravitational potential for most of the trip (c.f. Pound, Rebka). But also, contrastingly, the moving clocks were expected to age more slowly because of the speed of their travel. The gravitational effect was the larger, and the clocks suffered a net gain in elapsed time. To within experimental error, the net gain was consistent with the difference between the predicted gravitational gain and the predicted velocity time loss. In 2005, the National Physical Laboratory in the United Kingdom reported their limited replication of this experiment[1]. The NPL experiment differed from the original in that the cesium clocks were sent on a shorter trip (London-Washingon D. C. return), but the clocks were more accurate. The reported results are within 4% of the predictions of relativity.
- The Global Positioning System can be considered a continuously operating experiment in both special and general relativity. The in-orbit clocks are corrected for both special and general relativistic time-dilation effects so they run at the same (average) rate as clocks at the surface of the Earth. In addition, but not directly time-dilation related, general relativistic correction terms are built into the model of motion that the satellites broadcast to receivers — uncorrected, these effects would result in an approximately 7-metre oscillation in the pseudo-ranges measured by a receiver over a cycle of 12 hours.
[edit] Time dilation and space flight
Time dilation would make it possible for passengers in a fast moving vehicle to travel further into the future while aging very little, in that their great speed retards the rate of passage of onboard time. That is, the ship's clock (and according to relativity, any human travelling with it) shows less elapsed time than stationary clocks. For sufficiently high speeds the effect is dramatic. For example, one year of travel might correspond to ten years at home. Indeed, a constant 1 g acceleration would permit humans to travel as far as light has been able to since the big bang (some 13.7 billion light years) in one human lifetime. The space-travellers could return to earth billions of years in the future (provided the Universe hadn't collapsed and our solar system was still around, of course). A scenario based on this idea was presented in the novel Planet of the Apes by Pierre Boulle.
A more likely use of this effect would be to enable humans to travel to nearby stars without spending their entire lives aboard the ship. However, any such application of time dilation would require the use of some new, advanced method of propulsion. A further problem with relativistic travel is that at such velocities dispersed particles in the rarefied interstellar medium would turn into a stream of high-energy cosmic rays that would destroy the ship unless extraordinary radiation protection measures were taken. Strong electromagnetic fields that could ionize and deflect any interstellar matter has been suggested as one way to avoid these potentially disastrous consequences.
Current space flight technology has fundamental theoretical limits based on the practical problem that an increasing amount of energy is required for propulsion as a craft approaches the speed of light. The likelihood of collision with small space debris and other particulate material is another practical limitation. At the velocities presently attained, however, time dilation is not a factor in space travel. Travel to regions of spacetime where gravitational time dilation is taking place, such as within the gravitational field of a black hole but outside the event horizon (perhaps on a hyperbolic trajectory exiting the field), could also yield results consistent with present theory.
[edit] Time dilation at constant acceleration
In Special Relativity, time dilation is most simply described in circumstances where relative velocity is unchanging. Nevertheless, the Lorentz equations allow one to calculate proper time and movement in space for the simple case of a spaceship whose acceleration, relative to some referent object in uniform (ie, unaccelerating) motion, equals g throughout the period of measurement.
Let t be the time in an inertial frame subsequently called the rest frame. Let x be a spatial coordinate, and let the direction of the constant acceleration as well as the spaceship's velocity (relative to the rest frame) be parallel to the x-axis. Assuming the spaceship's position at time t = 0 being x = 0 and the velocity being v0, the following formulas hold [2]:
Position:
Velocity:
Proper time:
Time in the rest frame as a function of x:
[edit] Simple inference of time dilation
Time dilation can be inferred from the constancy of the speed of light in all reference frames as follows:
Consider a simple clock consisting of two mirrors A and B, between which a photon is bouncing. The separation of the mirrors is L, and the clock ticks once each time it hits a given mirror.
In the frame where the clock is at rest (diagram at right), the photon traces out a path of length 2L and the period of the clock is 2L divided by the speed of light.
From the frame of reference of a moving observer (diagram at lower right), the photon traces out a longer, angled, path. The second postulate of special relativity states that the speed of light is constant in all frames, which implies a lengthening of the period of this clock from the moving observer's perspective. That is to say, in a frame moving relative to the clock, the clock appears to be running slower. Straightforward application of the Pythagorean theorem leads to the well-known prediction of special relativity.
[edit] Time dilation is symmetric between two inertial observers
One assumes, naturally enough, that if time-passage has slowed for a moving object, the moving object would find the external world to be correspondingly "sped up." But counterintuitively, Einsteinian relativity predicts the opposite, a situation difficult to visualize. This is based on an essential principle of the overall theory: if one object is moving with respect to another (at an unchanging velocity), the other is equally moving with respect to it.
We're accustomed to this notion of relativity with respect to distance: the distance from Los Angeles to New York is, and must be, the same as the distance from New York to Los Angeles. But when we consider speeds, we think of an object as "really" moving, overlooking that its motion is always relative to something else — to oneself, the ground, the stars, etc. A camera dollying along with a moving object against a blank background would reveal no motion.
The Einsteinian takes seriously the thesis that all motion is indeed relative to some actual (if specified only by implication) "benchmark" that is regarded as stationary, setting aside any issue as to whether what is treated as stationary "really is". You regard it as stationary, and are justified in so treating it, if you yourself are maintaining a fixed distance from it. And this is true even if, for someone else, both you and the benchmark are moving along side-by-side.
But if motion is thus understood as purely relative, it can be divided-up between "mover" and "benchmark" in any way one pleases, even allowing them to completely switch roles. All that matters is the rate at which they are approaching, or departing from, one another, a grand total which re-distributing the speed-contribution of each one doesn't change. And if that is true, the consequences of relative motion predicted by the theory must also "add up" to an unchanging total effect. If A finds that B has undergone a slowdown-in-time during the period of relative motion, it must work out that B will also find that A has a relatively slower "clock." It seems an inconceivable situation: yet the math works out, and actual tests confirm it.
With respect to constant relative motion between two "clocks", a measurement of relative time must choose one clock as being "stationary" in spacetime, and that clock is the basis of a temporal coordinate system where time throughout is treated as synchronized with the stationary clock. The other "moving" clock is in motion with respect to this treated-as-stationary coordinated system, and its relative motion is the velocity value used in the applicable equations.
In the Special Theory of Relativity, the moving clock is found to be ticking slow with respect to the temporal coordinate system of the stationary clock. And as indicated, this effect is symmetrical: In a coordinate system synchronized, by contrast, with the "moving" clock, it is the "stationary" clocks that is found (by all methods of measurement) to be running slow. (Neglecting this principle of symmetry leads to the so-called twin paradox being regarded as paradoxical.)
Note that in all such attempts to establish "synchronization" within the reference system, the question of whether something happening at one location is in fact happening simultaneously with something happening elsewhere, is of key importance. Calculations are ultimately based on determining what is simultaneous with what.
It is a natural and legitimate question to ask how, in detail, Special Relativity can be self-consistent if clock A is time-dilated with respect to clock B and clock B is also time-dilated with respect to clock A. It is by challenging the assumptions we build into the common notion of simultaneity that logical consistency can be restored. Within the framework of the theory and its terminology, the short answer is that there is a relativity of simultaneity that affects how the specified "benchmark" moments of "simultaneous" events are aligned with respect to each other by observers who are in motion with respect to one other. Because the pairs of putatively simultaneous moments are differently identified by the different observers (as illustrated in the twin paradox article), each can treat the other clock as being the slow one without Relativity being self-contradictory. For those seeking a more explicit account, this can be explained in many ways, some of which follow.
[edit] Temporal coordinate systems and clock synchronization
In Relativity, temporal coordinate systems are set up using a procedure for synchronizing clocks, discussed by Poincaré (1900) in relation to Lorentz's local time (see relativity of simultaneity). It is now usually called the Einstein synchronization procedure, since it appeared in his 1905 paper.
An observer with a clock sends a light signal out at time t1 according to his clock. At a distant event, that light signal is reflected back to, and arrives back to the observer at time t2 according to his clock. Since the light travels the same path at the same rate going both out and back for the observer in this scenario, the coordinate time of the event of the photon being reflected for the observer tE is tE = (t1 + t2) / 2. In this way, a single observer's clock can be used to define temporal coordinates which are good anywhere in the universe.
Symmetric time dilation occurs with respect to temporal coordinate systems set up in this manner. It is an effect where another clock is being viewed as running slow by an observer. Observers in rest in their coordinate system do not consider their own clock time to be time-dilated, but may find that it is understood to be time-dilated in another coordinate system.
[edit] The spacetime geometry of velocity time dilation
The green dots and red dots in the animation represent spaceships. The ships of the green fleet have no velocity relative to each other, so for the clocks onboard the individual ships the same amount of time elapses relative to each other, and they can set up a procedure to maintain a synchronized standard fleet time. The ships of the "red fleet" are moving with a velocity of 0.866 of the speed of light with respect to the green fleet.
The blue dots represent pulses of light. One cycle of light-pulses between two green ships takes two seconds of "green time", one second for each leg.
As seen from the perspective of the reds, the transit time of the light pulses they exchange among each other is one second of "red time" for each leg. As seen from the perspective of the greens, the red ships' cycle of exchanging light pulses travels a diagonal path that is two light-seconds long. (As seen from the green perspective the reds travel 1.73 (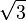 ) light-seconds of distance for every two seconds of green time.)
) light-seconds of distance for every two seconds of green time.)
One of the red ships emits a light pulse towards the greens every second of red time. These pulses are received by ships of the green fleet with two-second intervals as measured in green time. Not shown in the animation is that all aspects of physics are proportionally involved. The lightpulses that are emitted by the reds at a particular frequency as measured in red time are received at a lower frequency as measured by the detectors of the green fleet that measure against green time, and vice versa.
The animation cycles between the green perspective and the red perspective, to emphasize the symmetry. As there is no such thing as absolute motion in relativity (as is also the case for Newtonian mechanics), both the green and the red fleet are entitled to consider themselves as "non-moving" in their own frame of reference.
Again, it is vital to understand that the results of these interactions and calculations reflect the real state of the ships as it emerges from their situation of relative motion. It is not a mere quirk of the method of measurement or communication.
[edit] Time dilation in popular culture
| Trivia sections are discouraged under Wikipedia guidelines. The article could be improved by integrating relevant items into other sections and removing inappropriate items. (August 2007) |
- Time dilation caused by long distance space flight is central to L. Ron Hubbard's Return to Tomorrow (1954), Joe Haldeman's novel The Forever War (1975), as well as Orson Scott Card's Ender (c. 1985) novels. Andrew Wiggin, for example, is kept young through frequent time-dilative jumps.
- Time dilation underlies the theme song of the cult movie Dark Star, "Benson, Arizona". The lyrics are a lament of a space traveler separated from his lover by space and time.
- In the conclusion of Close Encounters of the Third Kind, humans "abducted" by the aliens are returned to earth, apparently unaged since the time of their abduction.
- Relativistic time dilation is used in Flight of the Navigator as the central plot conflict solved by a time travel jump to restore David to his proper time.
- Time dilation is a theme in the song "'39" by Queen.
- Mostly in Japan, time dilation is commonly called the Urashima effect, after Urashima Tarō.
- In the series Stargate SG-1, a time dilation device is used by the Asgard aliens to try to contain the robotic Replicators. The Replicators then use the device to strengthen their own forces, advancing by centuries in what is months to the rest of the universe.
- Another episode of Stargate SG-1 has a time dilation effect being created when a stargate connection is made to a planet being devoured by a black hole.
- In the final episode of Stargate SG-1, the time dilation device created by the Asgard is used to encompass the Odyssey to prevent an Ori energy beam from destroying the ship. As the beam is about hit, time outside the ship seems to stop, while time seems to pass normally for the passengers inside. This gives them more time to come up with a way to somehow escape the beam.
- Time dilation was also put into use in the Original Video Animation, Aim for the Top! Gunbuster. As a result of traveling at the speed of light during the struggle against the space monsters, the two heroines of the show barely age at all while several years pass on Earth.
- Time dilation plays an integral part of the story in the short anime film Voices of a Distant Star. Young lovers are separated when one decides to enlist in a six month tour of the galaxy and the other ages many years.
- Time dilation is shown in the 1968 film, Planet of the Apes. During the introduction, Taylor mentions that because his ship is going near the speed of light, he has aged only months and everyone he knew on Earth is now long dead.
- Time dilation is shown in the TV series, Andromeda. In the first episode of the series, Captain Dylan Hunt and his artificially intelligent ship, the Andromeda Ascendant, are trapped in time at the event horizon of a black hole. Due to the artificial gravity used on the ship reacting with the gravity of the singularity, time dilation occurs, visible as sections of action [a fight scene] slowing down. (Erroneously, the characters are aware of the time dilation, which shouldn't actually happen: time would flow consistantly in their perception.)
- Time dilation is the main plot element in Poul Anderson's novel, Tau Zero. A group of human scientists enroute to a local star system experience numerous engine problems with their starcraft. They are stuck accelerating toward the speed of light as they traverse the cosmos, aging only a few years while Earth is billions of years long dead.